A Primer on Nvidia's Embedded AI Market Prospects
We pick Nvidia (NVDA) as the first company that is going to benefit from embedded AI, as they provide a complete set of picks and shovels that provide the brains for humanoid robots:
Isaac Robotics Platform Now Provides Developers New Robot Training Simulator, Jetson Thor Robot Computer, Generative AI Foundation Models, and CUDA-Accelerated Perception and Manipulation Libraries
Isaac Platform
Nvidia's Isaac Platform is a comprehensive AI robotics development suite that provides the tools, libraries, simulation environments, and AI models needed to accelerate the creation, training, testing, and deployment of intelligent robots across a wide range of applications—including autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), robotic arms, and humanoids. It consists of multiple elements:
Isaac Libraries and AI Models are CUDA-accelerated and optimized for perception, planning, and control, and facilitate efficient development, training, simulation, deployment, and optimization across various robot types.
Isaac ROS is a collection of CUDA-accelerated packages and AI models built on the Robot Operating System 2 (ROS 2), enabling the streamlining of the creation of advanced robotics applications. Isaac ROS includes ready-to-use packages for common robotic tasks like navigation and perception, and it is deployable on embedded systems such as Nvidia Jetson.
Isaac Manipulator and Perceptor. Isaac Manipulator provides tools for developing AI-powered robotic arms capable of perceiving and interacting with their environments. Isaac Perceptor offers tools for the rapid development of advanced AMRs designed to operate in unstructured environments like warehouses and factories.
Isaac GR00T is a research initiative and development platform focused on general-purpose robot foundation models and data pipelines, with a particular emphasis on accelerating the development of humanoid robotics.
Isaac Sim serves as a high-fidelity simulation environment built on Nvidia Omniverse. It allows developers to simulate, test, and validate AI-driven robotics solutions in physically accurate virtual worlds. Isaac Sim supports synthetic data generation, sensor simulation (including vision, lidar, radar, and IMU), and the creation of digital twins for industrial facilities. It is used for software-in-the-loop testing, robot learning, and bridging the gap between simulation and real-world deployment. Training in simulation reduces reliance on costly physical hardware and enables 10,000x faster training cycles (which boils down to one year of training condensed to one hour on a single GPU).
Isaac Lab is an open-source, unified framework for robot learning built on Isaac Sim. It provides GPU-accelerated simulation for reinforcement learning, imitation learning, and policy training. Isaac Lab enables fast and scalable training of robot policies and supports a wide range of robot types and environments.
Let's start with the foundation model.
Foundation models
A foundation model for embedded AI, like Nvidia's GR00T, is like an LLM, but there are important differences:
Standard LLMs (like ChatGPT 5) are optimized for text-based reasoning and generation, enabling tasks like conversation, summarization, and code generation in purely virtual settings.
Embodied AI foundation models like GR00T are designed to control robots: they combine language understanding, vision, and physical action/planning to perform tasks in the real world, such as manipulating objects or navigating environments.
Embodied models unify vision, language, and action in a single policy, enabling robots to interpret human instructions, sense their surroundings, and act accordingly.
GR00T follows a dual-system architecture: one component enables fast, reflexive actions (akin to human intuition), while another supports slow, deliberative reasoning (planning, long-horizon tasks).
Traditional LLMs do not have this explicit split and are not structured around sensorimotor control, but rather around modeling sequential language.
LLMs are trained on large internet text corpora, so they capture linguistic and world knowledge about facts, reasoning, and relationships in text.
GR00T uses a mix of synthetic, simulated, and real-world datasets—including egocentric human videos, robot sensor data, and vision-language-action experiences—designed to ground linguistic instructions to physical outcomes.
This enables embodied models to generalize across robot platforms (cross-embodiment), tasks, and environments in ways that are necessary for real-world operation.
GR00T N1
Project GR00T enables robots to understand natural language and mimic human movements by observing human actions which:
will allow the robots to quickly learn coordination, dexterity, and other skills necessary to navigate, adapt, and interact with the real world.
And here is CEO Jensen Huang:
“Building foundation models for general humanoid robots is one of the most exciting problems to solve in AI today,” said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA. “The enabling technologies are coming together for leading roboticists around the world to take giant leaps towards artificial general robotics.”
GR00T N1 is an open, vision-language-action (VLA) foundation model designed for humanoid robots. It is trained on a vast mix of real robot trajectories, human demonstration videos, and synthetic data, giving it the ability to generalize across a wide range of tasks and environments.
Its dual-system architecture mimics human cognition:
System 2 (slow thinking) interprets vision and language, reasons about instructions, and plans actions.
System 1 (fast thinking) translates those plans into precise, real-time motor actions
This architecture allows robots to not only understand and execute complex, multi-step tasks, but also to adapt to new situations without needing to be explicitly reprogrammed for each scenario. What this delivers is humanoid robots that:
Are trained on a wide library of situations (real-world or synthetic).
Can make sense of its surroundings as it merges the signals from various sensors.
Can strategize and plan actions.
Can interact with humans as they can process natural language.
Can quickly adapt to new situations.
From Nvidia:
Preprogrammed robots operate using fixed instructions within set environments, which limits their adaptability to unexpected changes. AI-driven robots address these limitations through simulation-based learning, allowing them to autonomously perceive, plan, and act in dynamic conditions. With robot learning, they can acquire and refine new skills by using learned policies—sets of behaviors for navigation, manipulation, and more—to improve their decision-making across various situations.
Isaac Lab
Isaac Lab is Nvidia’s flagship robot learning framework, providing an open-source, flexible, and scalable platform for developing, training, and testing intelligent robotic systems in simulation, focusing especially on accelerating sim-to-real transfer.
Built on Jetson-optimized frameworks.
Enables developers to train robots in high-fidelity simulations (via Nvidia Omniverse and Nvidia Isaac Sim) using synthetic data.
Simulation training reduces reliance on costly physical hardware and enables 10Kx faster training cycles (e.g., one year of training condensed to one hour on a single GPU).
Simulated data gets around the limited availability of useful training data for humanoid robots, producing exponentially large amounts of synthetic motion trajectories for robot manipulation from just a few human demonstrations.
Its modular design empowers users to efficiently build, customize, and scale robot learning projects by providing interchangeable, extensible components and workflows (plug and play)
Learning and improving
These Nvidia solutions and platforms empower robots with AI-based brains that enable them to rapidly advance. GR00T N1 allows robots to not only understand and execute complex, multi-step tasks but also to adapt to new situations without needing to be explicitly reprogrammed for each scenario.
Together, they greatly facilitate the generation of training data, translating these results into robot skills and learning, and making these skills more easily transferable.
Nvidia Jetson platforms (including the upcoming Jetson Thor) provide the necessary edge computing power and functional safety to run complex AI models, like GR00T N1, directly on the robot, enabling them to process multimodal sensor data (vision, touch, language) in real time, learn from their own experiences, and adapt their behavior on the fly—without relying on constant cloud connectivity.
Robots can be post-trained with new data—either real or synthetic—enabling them to continuously improve and specialize for particular tasks or environments.
Cooperation
Nvidia is already cooperating with a host of robotics companies using their tools and platforms, like:
1x, Boston Dynamics, ByteDance Research, Field AI, Figure, Fourier, Galbot, LimX Dynamics, Mentee, Neura Robotics, RobotEra and Skild AI are among the first to join the early-access program.
Industry Adoption and Impact
Over 100 companies, including Siemens, BYD Electronics, Teradyne Robotics, and Intrinsic, are utilizing the Isaac Platform to develop, simulate, and deploy AI-enabled robots for manufacturing, logistics, and industrial automation (and this is data from January 2024).
The platform is modular, allowing companies to adopt individual components or the full stack depending on their needs.
Isaac technologies are credited with making factories, warehouses, and distribution centers more efficient, safer, and capable of automating tasks that were previously difficult or impossible to automate.
But none of this would work without some powerful onboard processing, which, of course, is also the forte of Nvidia, which has developed a computing platform for embedded AI called Jetson Thor.
Jetson Thor
Jetson Thor is Nvidia’s next-generation computing platform, specifically designed for AI-powered humanoid robots (part of the Jetson line of compact computers built for AI applications).
Jetson Thor was launched in June 2025. It represents a major leap forward in robotics computing, built on Nvidia's latest Blackwell GPU architecture and featuring the new Thor system-on-a-chip (SoC).
Jetson Thor is designed to power humanoid robots capable of complex tasks, natural interaction with humans and machines, and autonomous navigation. It supports advanced AI capabilities such as real-time object recognition, natural language processing, and generative AI integration, leveraging Nvidia's Project GR00T foundation model for humanoid robots. This project enables robots to understand natural language, mimic human movements, and quickly learn skills like coordination and dexterity by observing humans.
Nvidia positions Jetson Thor not as a robot maker but as a technology partner providing the brains behind robots built by other manufacturers, collaborating with companies like Siemens, Universal Robots, Boston Dynamics, and others. This approach aims to accelerate the development of humanoid robots across industries such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing.
Technical Specifications
Jetson Thor delivers an 8x improvement in GPU performance over its predecessor, the Jetson AGX Orin, thanks to the inclusion of a Transformer Engine supporting floating-point precisions from FP4 to FP16. The CPU performance is also boosted by approximately 2.6 times compared to Orin.
It supports up to 128 GB of LPDDR5X RAM with a 256-bit interface and about 273 GB/s bandwidth, doubling the memory capacity of Orin. The I/O bandwidth is increased tenfold, including advanced USB 4.0 support, new Wi-Fi, and high-speed Ethernet capabilities, with up to 100GB Ethernet bandwidth.
The system includes three GPCs with 2560 CUDA cores and 96 Tensor cores, enabling 7.8 TFLOPS FP32, 500 TOPS FP16, 1000 TOPS FP8, and 2000 TOPS FP4 AI performance. The CPU features 14 Poseidon-AE (Neoverse V3AE) cores with 1 MB L2 cache per core, totaling 14 MB L2 cache.
Jetson Thor incorporates an integrated functional safety processor and a modular architecture optimized for performance, power efficiency, and size, simplifying design and integration efforts for robotics developers.
Some of the key features:
High-Performance AI Computing – Capable of handling complex deep learning tasks with unmatched efficiency.
Low-Power Consumption – Optimized for long-term usage in robotic applications.
Advanced Sensor Integration – Supports vision, voice, and motion sensors to enhance robot interaction.
Compact & Scalable Design – Suitable for a variety of robotic applications, from industrial automation to consumer robotics.
Applications That Will Benefit Most from Jetson Thor
Nvidia's Jetson Thor is engineered to power the next generation of AI-driven robotics, with a particular focus on humanoid robots and advanced autonomous systems. Its AI computing power, real-time processing, and sensor integration make it especially impactful for several specific AI applications:
Real-Time Object Recognition and Perception: Jetson Thor's high-performance AI capabilities enable robots to process visual data from cameras and sensors in real time, allowing for advanced object detection, classification, and scene understanding, crucial for robots operating in dynamic environments, such as warehouses, hospitals, and homes.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Human-Robot Interaction: The platform supports sophisticated NLP, enabling robots to understand and respond to human speech, interpret commands, and engage in meaningful conversations. This enhances applications in customer service, healthcare assistance, and personal robotics, where intuitive interaction is essential.
Autonomous Navigation and Mobility: Jetson Thor facilitates real-time sensor fusion and decision-making, allowing robots to navigate complex, unstructured environments safely and efficiently. This is vital for autonomous mobile robots in logistics, manufacturing, and service industries.
Advanced Machine Learning and On-Device Training: Its powerful AI hardware allows robots to not only infer but also learn from new data on the edge. Robots can adapt to changing environments, improve their skills, and personalize their behavior without relying solely on cloud computing25.
Industrial Automation and Precision Tasks: In manufacturing and assembly lines, Jetson Thor enables robots to perform intricate, repetitive, or hazardous tasks with high precision and reliability, increasing efficiency and safety235.
Healthcare Robotics: Applications include robotic assistants for patient care, rehabilitation, and surgery. Jetson Thor’s ability to process multimodal sensor data and interact naturally with patients makes it highly suitable for healthcare environments45.
Generative AI and Adaptive Learning: The platform is optimized for deep learning and generative AI workloads, allowing robots to learn new skills, generate responses, and adapt to novel scenarios. This supports the development of general-purpose humanoid robots capable of performing a wide variety of tasks35.
Surveillance, Security, and Defense: Robots powered by Jetson Thor can analyze video feeds, detect anomalies, and respond to security threats in real time, enhancing surveillance and reconnaissance operations.
Emerging industry standard?
There is growing evidence that Nvidia's ISAAC platform, GR00T foundation model, and Jetson Thor processor are becoming the industry standard for robotics and embodied AI development, with widespread adoption across major robotics companies and partnerships.
Nvidia’s integration of high-performance edge silicon, full-stack software, and developer outreach through CUDA makes it a default supplier in many emerging AI-robotics verticals, insulating its prospects from pure hardware competition.
For instance, big robotics companies are making extensive use of some or all of Nvidia's robotics offerings.
Boston Dynamics has expanded its collaboration with Nvidia to integrate Jetson Thor into its humanoid robot Atlas, calling it a key step toward building "the world's most capable humanoid". The partnership involves using Isaac Lab for developing state-of-the-art AI capabilities, with Aaron Saunders, Boston Dynamics' CTO, stating that early results are "exciting".
Amazon has deployed Nvidia Isaac Sim extensively for its Proteus autonomous warehouse robot, achieving a 98% marker detection success rate (up from 88.6%) using synthetic data generation. Amazon Robotics uses Isaac to generate over 50K synthetic images for training AI models and has implemented zero-touch manufacturing using Nvidia digital twin technologies.
Agility Robotics has integrated Jetson into its fifth-generation Digit robot and plans to adopt Jetson Thor as the onboard compute platform for Digit's sixth generation, with CEO Peggy Johnson noting that Thor will "take Digit to the next level".
Over 2 million developers are now using Nvidia's robotics stack, representing massive developer community adoption. More than 100 companies are using Isaac Sim for robotics simulation and testing, from Nvidia:
Early adopters include industry leaders Agility Robotics, Amazon Robotics, Boston Dynamics, Caterpillar, Figure, Hexagon, Medtronic and Meta, while 1X, John Deere, OpenAI and Physical Intelligence are evaluating Jetson Thor to advance their physical AI capabilities.
Leading humanoid developers adopting GR00T N1 include Agility Robotics, Fourier, Foxlink, Galbot, Mentee Robotics, NEURA Robotics, General Robotics, Skild AI, and XPENG Robotics. Early GR00T adopters also include AeiRobot, Lightwheel, and others using the models for industrial applications.
At major trade shows like Automatica 2025 and Automate 2025, Taiwanese suppliers like Advantech, NEXCOM, and Solomon showcased products built on Jetson Thor. European robotics developers are extensively integrating Isaac platform technologies.
Isaac Sim is now available on AWS with L40S GPUs, providing doubled performance and enabling robotics startups like Field AI, Vention, and Cobot to leverage cloud-based development.
Nvidia announced collaborations with Google DeepMind and Disney Research to develop Newton, an open-source physics engine for robot learning, with MuJoCo-Warp expected to accelerate robotics ML workloads by more than 70x.
Comprehensive Ecosystem
Nvidia's three-computer approach (DGX for training, Omniverse/OVX for simulation, Jetson for deployment) is seeing significant adoption, with companies following this standardized architecture.
Revenue prospects
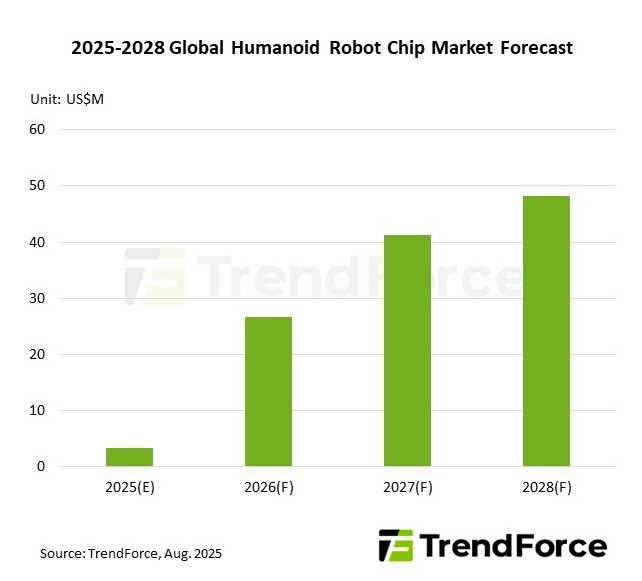
Nvidia's robotics segment is growing 72% year-over-year and is projected to become a $10B+ revenue line by 2030. The humanoid robot chip market is projected to surpass $48M by 2028.
It has to be stressed that this $48M projection by 2028 shows that things are still in the very early stages.
Industry forecasts expect rapid market growth for embedded AI, driven by adoption in robotics, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and industrial automation, areas where Nvidia's Jetson and Thor platforms are positioned to lead.
The global embedded AI market is projected to grow from around $12B billion in 2025 to $23–30B by 2030, at a CAGR above 14%.
Nvidia is expected to capture a significant share due to its early mover advantage, deep developer ecosystem, and expanding Jetson product line, especially as advanced robotics, edge AI, and autonomous platforms become mainstream in logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare.
CEO Jensen Huang has stated that robotics and edge AI represent a multi-trillion dollar total addressable market over time, although near-term revenue will scale more gradually as deployments ramp and more customers transition from pilot projects to volume production.
Investors should watch for signs of subscription-based software and platform revenues layered atop Jetson hardware, which could accelerate growth and improve margins for this segment over time.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s embedded AI solutions empower humanoid robots to automatically learn, adapt, and improve by combining powerful on-device AI, generalist foundation models, scalable simulation, and continual post-training.
These combined solutions enable robots to handle new tasks, environments, and user preferences with minimal human intervention, putting customers on the road towards building adaptable, self-improving humanoid robots.
We're not quite there yet, but Nvidia is very well placed to capture a large slice of the embedded AI market due to its extensive product offerings, excellent hardware, and CUDA's entrenched user basis.